

In water, sodium chloride (NaCl), dissociates into the sodium ion (Na +) and the chloride ion (Cl –). Transport of Electrolytes across Cell MembranesĮlectrolytes, such as sodium chloride, ionize in water, meaning that they dissociate into their component ions. Because blood plasma is one of the fluid components, osmotic pressures have a direct bearing on blood pressure. Since osmotic pressure is regulated by the movement of water across membranes, the volume of the fluid compartments can also change temporarily. Mammalian systems have evolved to regulate not only the overall osmotic pressure across membranes, but also specific concentrations of important electrolytes in the three major fluid compartments: blood plasma, extracellular fluid, and intracellular fluid. Without a mechanism to regulate osmotic pressure, or when a disease damages this mechanism, there is a tendency to accumulate toxic waste and water, which can have dire consequences. Need for Osmoregulationīiological systems constantly interact and exchange water and nutrients with the environment by way of consumption of food and water and through excretion in the form of sweat, urine, and feces. While osmoregulation is achieved across membranes within the body, excess electrolytes and wastes are transported to the kidneys and excreted, helping to maintain osmotic balance. There is a constant input of water and electrolytes into the system. Isotonic cells have an equal concentration of solutes inside and outside the cell this equalizes the osmotic pressure on either side of the cell membrane which is a semi-permeable membrane.

A cell placed in a solution with higher salt concentration, on the other hand, tends to make the membrane shrivel up due to loss of water into the hypertonic or “high salt” environment. (credit: Mariana Ruiz Villareal)Īs seen in Figure 1, a cell placed in water tends to swell due to gain of water from the hypotonic or “low salt” environment. The blood maintains an isotonic environment so that cells neither shrink nor swell. In a hypotonic environment, cells tend to swell due to intake of water. Solutions on two sides of a semi-permeable membrane tend to equalize in solute concentration by movement of solutes and/or water across the membrane.įigure 1. Cells placed in a hypertonic environment tend to shrink due to loss of water. Semi-permeable membranes are permeable (or permissive) to certain types of solutes and water. The membranes of the body (such as the pleural, serous, and cell membranes) are semi-permeable membranes. The body’s fluids include blood plasma, the cytosol within cells, and interstitial fluid, the fluid that exists in the spaces between cells and tissues of the body. Both electrolytes and non-electrolytes contribute to the osmotic balance. A non-electrolyte, in contrast, doesn’t dissociate into ions during water dissolution.
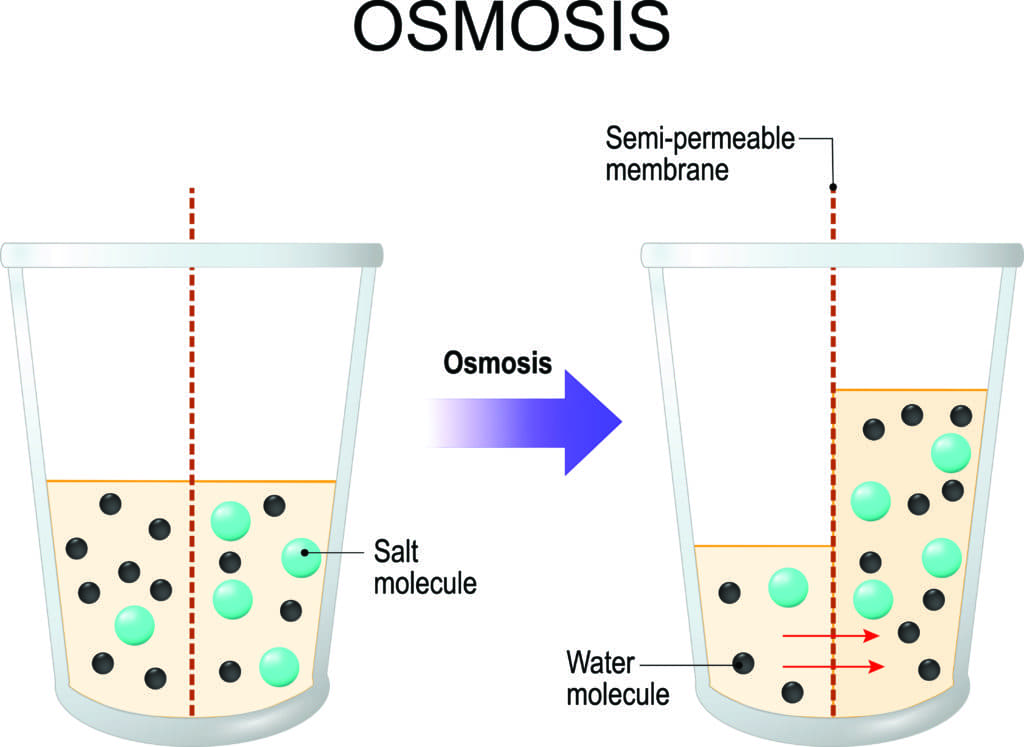
An electrolyte is a solute that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water.
Osmosis in er lumen plus#
Osmoregulation is the process of maintenance of salt and water balance ( osmotic balance) across membranes within the body’s fluids, which are composed of water, plus electrolytes and non-electrolytes. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane in response to osmotic pressure caused by an imbalance of molecules on either side of the membrane. Describe osmoregulators or osmoconformers and how these tools allow animals to adapt to different environments.Explain osmolarity and the way in which it is measured.Explain why osmoregulation and osmotic balance are important body functions.Define osmosis and explain its role within molecules.By the end of this section, you will have completed the following objectives:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
